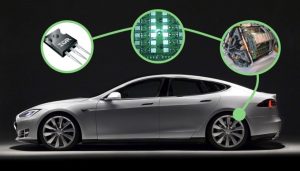
IGBT power modules (inverters) are needed to convert electricity from one form to another so that the electricity can be conveniently and safely used by many of the things we use in our everyday lives; including air conditioners, refrigerators, electric cars, and more.
Learn more about IBGT, including how they work and what it takes to manufacture them below.
What’s an IGBT?
IGBT is the short form of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor. It is a three-terminal power semiconductor device primarily used as an electronic switch. These devices- integrated as part of an IGBT power module- are ideal for today’s electronic devices because of their ability to quickly turn the flow of power flow on/off.
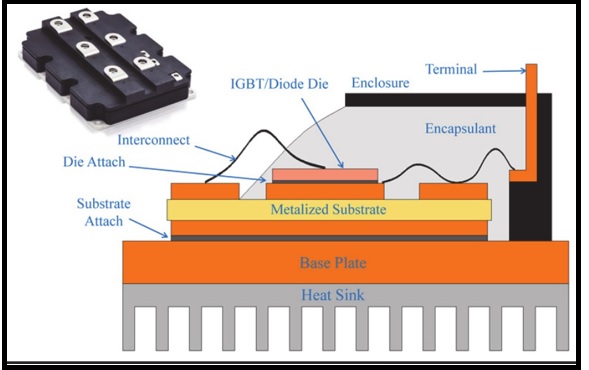
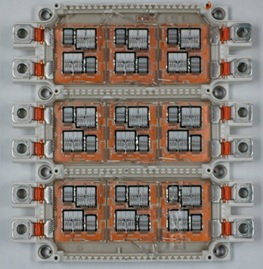
An IGBT power module is an assembly and physical packaging of several IGBT power semiconductor dies in one package.
IGBTs are found in electric cars, variable-frequency drives (VFDs) trains, variable speed refrigerators, lamp ballasts, air conditioners, military applications, and just about any electronic device that requires high-speed switching of current.
What does an IGBT module do?
An IGBT power module functions as an electronic switching device allowing the current to switch from DC to AC. By alternate switching direct current (DC) can be transformed into alternating current (AC) and vice-versa.
Imagine you’re a DC battery and someone taps you on the shoulder and asks you to produce AC instead. How would you do it? If all the current you produce flows out in one direction, what about adding a simple switch to your output lead? Switching your current on and off, very rapidly, would give pulses of direct current. To make proper AC, you’d need a switch that allowed you to reverse the current and do it about 100 times every second. Visualize yourself as a human battery swapping your contacts back and forth over 6000 times a minute. Now that’s a lot of switching. Luckily for us, the IGBT power module can easily take over that job for us. . . .
This power conversion is important for the applications to function correctly. For example, in order to drive an electric motor, 3 phase AC current is needed. While on the other end, all electrical energy storage systems (batteries) need DC current. IGBT modules play an integral role in making this happen.
IGBT and Electric Cars
In electric cars, the IGBT power module is considered the ‘heart’ of the electrified drive train.
Similar to a heart distributing energy throughout our bodies, the power module functions as the human heart in the electric drive train for electric and hybrid-electric vehicles. In the electric drive train, the power module distributes and converts the DC current from the electric vehicle battery to AC current to be used in the electric motor driving the vehicle propulsion system. That makes the power module a critical component in improving energy efficiency and battery range for electrical cars.
What’s inside an IGBT Power Module Unit?
The image below is an exploded view of the typical elements of an IGBT module, which may include: several power module boards, plastic housing, heatsink, layers of silicone and/or glue, and a gel layer (to help with heat dissipation). All of this is then placed inside the housing assembly and the pieces of the assembly are attached together to create the final assembled unit.
Let’s break down these elements and talk about some of the manufacturing challenges.
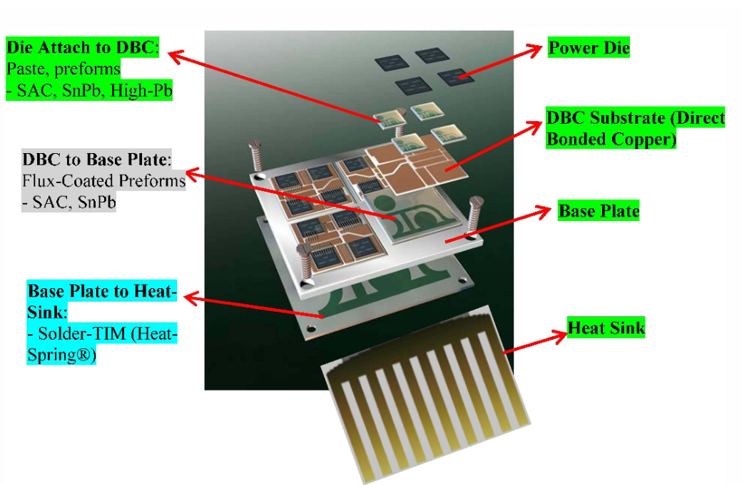
Power Module Board
The power module board, which is typically a Direct Bonded Copper substrate (DBC substrates are commonly used in power modules, because of their very good thermal conductivity. ) requires multiple types of die and solder preform attach. Processes may include: IGBT die-attach, diode die-attach, SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) / Thyristor die-attach, solder preform attach, and capacitor and resistor placement.
What would be some of the challenges of manufacturing a board like this?
- Fragile die and substrate handling
- High-Mix component types
- High throughput demand
Our FuzionSC™ platform offers:
- High-mix, high-throughput all in one solution
- Ability to feed from wafer, tape, tray
- 10um High accuracy, 10g~5000g force placement capability
- 200um x 200um ~ 150mm x 150mm component range
- Substrate handler vacuum support
See FuzionSC below demonstrating – DBC placement, preform & die placement.
Assembly of the IGBT Module
As we mentioned above, the boards (typically 3 go into 1 IGBT unit) are only one part of the overall module. All of the separate pieces need to be assembled together and then integrated into the final housing. Odd-form automation processes may include: lead frame placement, DBC placement, aligner placement, heat sink attach, and gel layer assembly.
What might be some of the challenges?
- Large/ heavy odd-form parts
- High-mix packages (Tray, Waffle, Gel)
- High throughput demand
FuzionSC and/or FuzionOF™ can address these challenges with:
- Flexible material handling
- Variety of high-capacity feeding solutions
- Up to a 150mm x 150mm component range
- 10g~5000g force placement capability
See FuzionOF video below demonstrating a wide range of OF Automation processes.
Final Housing Assembly
Completion of the final assembly of the IGBT unit would require dispensing of silicone and gel, placing the IGBT module in the final housing, and attaching the top and bottom together by inserting and turning screws.
What might be some of the challenges?
- Large/ heavy parts
- Multi-process requirements
- High throughput demand
- Dispensing requirements
Our Ulflex platform features:
- Flexible material handling for large & heavy parts
- Dispensing of glue, gel, etc.
- Screw driving
- Multi-process capability
- Easy re-configurability
See Uflex™ video below demonstrating dispense and screw-driving:
No matter what your IGBT assembly challenges are including multiple component types, multiple component packaging types, production floor constraints, or high-volume demand, we have THE solution for you.
Reach out and let us know how we can help with your IGBT manufacturing needs!